A Complete Checklist and Guide on How to Start a Supermarket Business in India – 2026
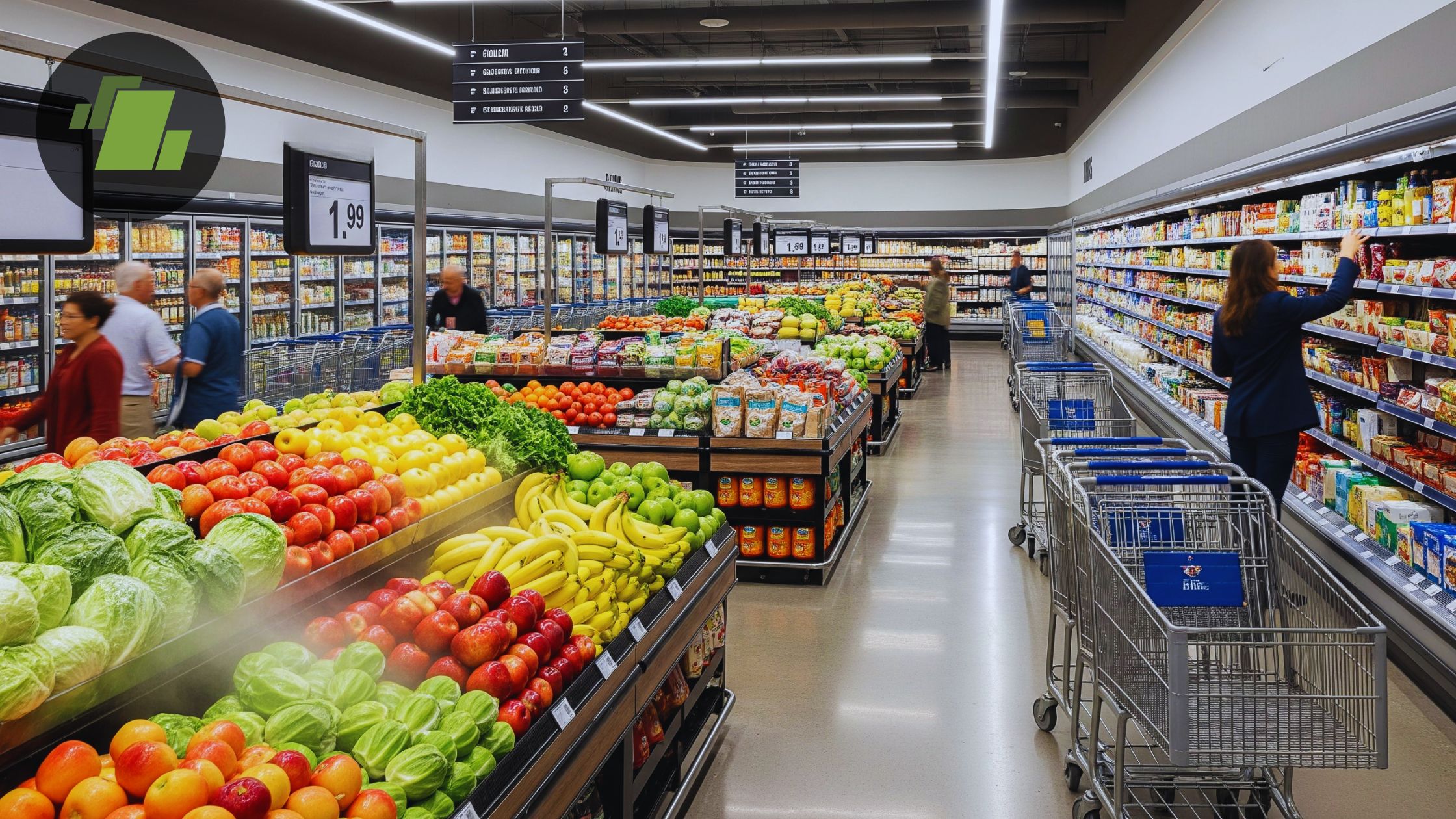

Introduction
Entering the Indian supermarket industry can be a profitable venture with the right planning, whether you are launching a small-scale supermarket or a large-scale FMCG supermarket. India’s retail sector is highly competitive, driven by increasing urbanization, changing consumer behavior, and government initiatives supporting organized retail. To succeed, it is important to have a comprehensive business plan of “how to start a supermarket business in India,” checklists for operational setup, documentation requirement, key licenses, location checklist, legal compliance, and technology adoption.
In this guide, we cover all aspects of starting a supermarket in India, including business registration, licenses, documentation, location and layout, standard operating procedures (SOPs), stocking strategies, software applications, equipment, marketing, pricing, and recruitment strategies. By following this roadmap, retailers and entrepreneurs can establish a successful and profitable supermarket business.
Table of Contents
- Business Plan and Capital Requirement Checklist of “How to Start a Supermarket Business?”
- List of Documents and Government Formalities Required
- Business Registration
- Licenses
- GST Registration
- Professional Tax Registration (PT)
- Checklist for Location and Layout
- Checklist for Establishing Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
- Checklist for Stocking Key Products
- Checklist for Software Applications in Supermarkets
- Checklist for Equipment Required for Supermarket Business
- Other Requirements
- Marketing and Advertising Strategies
- Pricing Strategy
- Recruitment Strategy
- Conclusion
Business Plan and Capital Requirement Checklist
For retailers and entrepreneurs planning to enter the supermarket sector in India, understanding how to start a supermarket business is the first crucial step. With the government introducing business-friendly policies, easier GST compliance, and support for organized retail, setting up a supermarket has become significantly smoother. By following a structured checklist that covers business registration, location selection, licenses, supermarket software solutions, and operational planning, you can build a supermarket that launches quickly, runs seamlessly, and stays profitable in the long run.
A detailed supermarket business plan serves as the foundation of a successful venture. It defines the scale of operations, capital requirements, product offerings, and growth strategies.
1. Define the Size and Scale of Your Supermarket
Decide whether you want to start a small neighborhood convenience store, a medium-sized supermarket, or a large-format FMCG supermarket with multiple product categories such as groceries, fresh produce, dairy, frozen food, personal care, household goods, and more. The size and scale will directly impact your investment, staffing, inventory, and store design.
2. Determine the Required Capital and Financing Options
Estimate the total investment needed to launch and run your supermarket. This includes planning your initial capital and exploring financing sources such as:
- Personal savings
- Bank loans
- MSME and government subsidy schemes
- Business investors or partners
- Overdraft facilities or working capital loans
A clear capital plan helps in maintaining cash flow and avoiding financial bottlenecks during setup.
3. Decide on the Ownership Structure
Choose the most suitable legal structure for your supermarket business based on your future growth plans and ease of compliance:
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership Firm
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
- One Person Company (OPC)
- Private Limited Company
Each structure has different tax implications, liability protections, and documentation requirements.
4. Identify Potential Brand Partnerships and Product Offerings
Building the right vendor and brand partnerships ensures consistent supply and better profit margins. Identify:
- FMCG brands you want to stock
- Wholesale suppliers and distributors
- Regional brands for local products
- Private label opportunities
- Seasonal and promotional product categories
This helps in offering variety, competitive pricing, and strong customer appeal.
5. Estimate the Total Capital Requirement
A supermarket requires investment across various operational and setup areas. Estimate costs under the following categories:
A. Setup Costs
-
- Leasing or renting the commercial property
- Interior design and store layout planning
- Purchase of shelves, racks, display units, and signage
- Installation of counters and point-of-sale areas
B. Initial Stock Purchase
- Buying inventory from FMCG vendors
- Stocking essential categories and high-demand items
- Fixing reorder levels to avoid stock-outs
C. Business Setup and Licensing Costs
- Business registration
- GST registration
- Shop and Establishment license
- FSSAI license
- Other regulatory permits applicable in your state
D. Technology and Equipment Investments
- CCTV surveillance systems
- POS billing counters and barcode scanners
- Supermarket software or ERP systems
- Computers, printers, and card-swiping machines
- RFID or handheld devices for stock management
E. Marketing and Advertising Costs
Allocate budget for:
- Newspaper ads
- Flyers and brochures
- Printed signboards
- Outdoor branding
- Grand opening promotions
- Loyalty programs and customer acquisition campaigns
6. Product and Brand Partnership Strategy
To build a strong market presence, partner with:
- Leading national FMCG brands
- Local wholesalers for competitive pricing
- Exclusive or niche brands for premium category customers
This ensures your supermarket is well-stocked, customer-friendly, and aligned with market demand.
List of Documents and Government Formalities Required
Legal compliance is mandatory when starting a supermarket in India.
Business Registration and Mandatory Licenses for Starting a Supermarket in India
Starting a supermarket in India requires completing several legal, regulatory, and documentation formalities. These ensure your business operates legally, builds customer trust, and complies with state and national retail laws. Below are all the essential points consolidated in a clear and organized format:
1. Business Registration
To officially launch your supermarket business, you must register your business entity under one of the legally recognized structures:
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership Firm
- One Person Company (OPC)
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
- Private Limited Company
Formal business registration grants your supermarket a legal identity, supports compliance, and improves credibility with customers, banks, and suppliers.
2. Mandatory Licenses Required
A. Shop and Establishment License
- Regulates working hours, employee conditions, wages, leaves, and safety.
- Mandatory for all retail establishments in India.
- Ensures your supermarket provides a fair and safe workplace.
B. FSSAI License
- Required because supermarkets sell packaged foods, dairy, bakery, snacks, and other consumables.
- Ensures the safety and quality of all food products stored and sold in the supermarket.
C. GST Registration
- Mandatory if turnover exceeds ₹40 lakh (or ₹20 lakh in special category states).
- Needed even earlier if your supermarket has multiple branches or engages in interstate movement of goods.
- Allows you to collect GST, claim input tax credit, and operate legally under the GST framework.
D. Import Export Code (IEC)
- Needed if your supermarket plans to import products (e.g., foreign snacks, chocolates, beverages, or packaged goods).
- Also required if you intend to export any items in the future.
E. Professional Tax Registration (PT)
- Levied on salaries paid to employees.
- Mandatory in most Indian states; exempt in states where PT is not applicable.
- Must file returns monthly or annually depending on state norms.
3. Documentation Requirements
To complete registrations and obtain licenses, the following documents are mandatory:
- PAN Card – For tax identification.
- Aadhar Card – Proof of identity and address.
- Utility Bills (within 3 months) – Electricity, water, or broadband bills as address proof.
- Bank Account Statement – Validates financial activity and business viability.
- Passport-sized Photograph – For owner identification.
- Incorporation Certificate – Required if registering as a Private Limited Company or LLP.
- GST Registration Certificate – Proof of GST compliance.
- Shop and Establishment Certificate – Validates business operation rights.
- FSSAI Certificate – Ensures food safety compliance.
Location & Layout Planning for Your Supermarket
Choosing the right location and designing an efficient store layout are two of the most crucial steps in launching a successful supermarket. Both elements directly influence customer experience, footfall, sales volume, and operational efficiency.
Location Planning: Key Considerations
- Conduct In-Depth Market Research
Analyse the locality for potential footfall, purchasing power, customer behavior, nearby competitors, and overall marketplace benefits. - Target High-Middle-Class Residential Areas
These areas offer stronger purchasing capacity, regular foot traffic, and higher demand for organized retail stores. - Look for Low Competition Zones
Prefer locations with fewer existing supermarkets to maximize market penetration and avoid immediate price wars. - Ensure Ample Parking Space
Easy parking for two-wheelers and four-wheelers improves customer convenience and increases store visits. - Check for Adequate Storage and Back-End Space
Proper storage is essential for managing inventory, especially for FMCG, staples, beverages, and perishable goods. - Evaluate Rent or Property Purchase Costs
Ensure that the monthly rent or investment aligns with your business budget and long-term financial projections. - Choose a Location With High Visibility & Easy Access
A store located near main roads, residential societies, public transport routes, or market hotspots attracts more visitors.
Store Layout Planning: Key Considerations
- Design a Clear and Functional Layout
Create a well-defined structure where products are displayed category-wise for easy navigation. - Organize Essential Categories Strategically
Group items such as staples, groceries, FMCG, personal care, beverages, snacks, dairy, and frozen foods in logical sections. - Ensure Wide Aisles
Maintain sufficient aisle width to allow customers with trolleys and baskets to move freely without congestion. - Use Clear Signage and Category Boards
Properly labeled shelves and aisle indicators improve customer experience and reduce time spent searching for products. - Avoid Cluttered Spaces
Keep shelves organized, displays neat, and pathways open to minimize confusion and enhance the shopping experience. - Strategically Position Billing Counters
Place checkout counters near exits to streamline customer flow and ensure faster billing and reduced waiting times. - Utilize Smart Merchandising Techniques
- Place high-demand items at the back to ensure customers walk through multiple aisles.
- Use end-cap displays to highlight offers and fast-moving products.
- Keep impulse-buy items like chocolates, gums, and small FMCG products near billing counters.
Checklist for Establishing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
In the dynamic and competitive landscape of the supermarket business, the implementation of robust Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) becomes the backbone of operational excellence. SOPs create a structured and uniform system that guides every employee, every department, and every process within the store. Much like meticulously designed flowcharts, SOPs break down complex activities into clear, actionable steps, ensuring that operations run smoothly even during peak hours or unexpected situations. They help different departments such as inventory, billing, customer service, and logistics, function in complete harmony by clearly defining interdependencies and communication pathways.
Beyond daily operations, SOPs act as a preventive mechanism, identifying potential loopholes that could lead to stock discrepancies, customer dissatisfaction, or financial losses. Their proactive nature helps supermarket owners handle challenges efficiently, reducing downtime and avoiding costly mistakes. By establishing standardized procedures, employees know exactly what needs to be done and how to do it, resulting in minimized errors, faster task completion, and consistent service quality across all shifts. Ultimately, strong SOPs create a disciplined work environment, reinforce accountability, and play a vital role in enhancing customer experience, profitability, and long-term scalability of the supermarket business.
SOPs ensure consistent operations and efficiency across all departments.
1. Inventory Management SOPs
- Guidelines for stocking shelves and timely replenishment.
- Monitoring product expiry dates and damaged goods.
- Preventing stockouts or overstocking with proper forecasting.
- Using FIFO/FEFO methods for inventory rotation.
- Regular inventory audits and cycle counts.
2. Customer Service SOPs
- Handling customer inquiries, complaints, and return requests.
- Maintaining a friendly, helpful, and professional approach.
- Processes for managing loyalty programs and customer engagement initiatives.
- Escalation procedures for unresolved customer issues.
3. Employee Training SOPs
- Clear description of each role and responsibility.
- Daily task checklists for cashiers, floor staff, and supervisors.
- Performance tracking and evaluation guidelines.
- Training modules for new hires and ongoing development programs.
4. Safety & Hygiene SOPs
- Floor safety protocols (spill management, hazard markings).
- Fire safety rules and emergency response procedures.
- Cleaning schedules for aisles, shelves, restrooms, and storage areas.
- Hygiene standards for handling perishables and FMCG items.
5. Cash Handling SOPs
- Billing procedures for accurate scanning and discount validation.
- Cash drawer management and drawer opening/closing rules.
- End-of-day cash reconciliation and reporting.
- SOPs to prevent discrepancies and ensure cashier accountability.
6. Marketing & Promotions SOPs
- Planning and execution of seasonal offers and marketing campaigns.
- Guidelines for in-store product displays and signage.
- Coordination between marketing, inventory, and floor staff.
- Event-based promotions and festival campaign checklists.
7. Technology Usage SOPs
- Proper use of POS systems for billing and data accuracy.
- Using ERP and inventory software to track real-time stock movement.
- Maintenance of hardware such as barcode scanners and printers.
- SOPs for security camera monitoring and data backup.
- Digital signage and automation tool usage guidelines.
Checklist for Stocking Key Products
Maintaining the right inventory is important for customer satisfaction and profitability.
Essential Product Categories:
- Staples: Rice, flour, pulses, sugar, salt.
- FMCG Products: Snacks, beverages, household items, personal care.
- Fresh Produce: Fruits, vegetables, dairy, meat (if permitted).
- Specialty Products: Organic, imported, or premium goods.
- Inventory Management: Track sales trends, optimize stock rotation, and prevent stock-outs.
Checklist for Software Applications in Supermarkets
Modern supermarkets depend heavily on ERP and POS systems to streamline billing, inventory, accounting, and multi-store operations. A thorough software checklist is crucial for choosing the right solution that ensures data accuracy, supports analytics, and empowers better decisions for sustainable business growth.
Software Considerations:
Choose a fast and reliable POS software that supports quick billing, multiple payment modes, barcode scanning, and generates GST-compliant invoices to ensure smooth checkout operations.
Invest in a robust supermarket ERP software that offers centralized management of accounting, billing, inventory, CRM, e-commerce, and multi-store synchronization, enabling seamless operations across all locations.
Ensure real-time data synchronization so sales, stock, pricing, and customer data are updated instantly across all stores through a centralized dashboard, reducing errors and improving accuracy.
Select software with strong inventory management features, including low-stock alerts, automated reordering, and product expiry/aging analysis, helping avoid stockouts and wastage.
Check analytics and reporting capabilities to generate actionable insights on sales trends, customer behavior, peak hours, product performance, and revenue patterns for data-driven decisions.
Verify scalability of the system so the software can accommodate future expansion—such as adding more stores, new billing counters, new product lines, or increased customer footfall.
Choose user-friendly software with an easy learning curve to ensure quick adoption by existing and new staff, minimizing training time and improving efficiency.
Ensure additional retail-focused features, such as loyalty program management, coupon and discount generation, membership management, and digital customer engagement tools.
Evaluate financial management tools within the software, including daily reconciliation, expense tracking, profitability reports, and vendor payments to maintain financial transparency.
Confirm support for operational processes, such as stock verification, shelf replenishment planning, purchase order generation, and supplier management.
Assess adaptability to industry changes, ensuring the software can integrate with modern technologies, such as mobile POS, cloud systems, digital payments, and online ordering.
Prefer an all-in-one integrated supermarket software solution instead of using multiple disconnected systems to maintain operational consistency and reduce technology overhead.
Checklist for Equipment Required
Sales Floor Equipment
- Open and close signboards, discount boards, and marketing banners.
- Counters and supporting counter equipment.
- Billing machines, POS systems, RFID scanners, handheld devices.
- Computers, card swiping machines, and tag machines.
- Security cameras and surveillance systems for store safety.
- Glass-door refrigerators for cold drinks and perishable products.
- Shopping carts, trolleys, and carry bags.
- Commercial display cases for premium and special products.
- Hanger stands for apparel, accessories, and organized product display.
- Quality fixtures, wall shelves, and storage racks.
- Mirrors of various sizes placed across the store for customer convenience.
Office & Break Room Equipment
- Office chairs, desks, stools, and essential seating furniture.
- Coffee machine, microwave oven for staff break room.
- Trash cans for waste management.
- Proper lighting, storage cabinets, and organized workspace essentials.
Other Operational Requirements | Marketing, Pricing, and Recruitment Strategy
Marketing & Advertising Strategy
- Analyze consumer preferences, product demand, and pricing trends before planning promotions.
- Study customer behavior to design effective marketing communication.
- Develop a marketing plan across both offline and digital channels.
- Use signage, banners, flyers, social media ads, and local promotions.
- Plan grand opening events to attract initial footfall.
- Offer early-bird discounts, limited-period deals, and trial offers.
- Introduce loyalty programs, reward points, and membership cards to retain customers.
Pricing Strategy
A well-planned pricing approach helps attract customers, stay competitive, and ensure profitability.
Key Points
- Determine the complete product range you will offer across categories.
- Create a pricing strategy for different product classes (FMCG, fresh produce, beverages, staples, premium items, etc.).
- Conduct market surveys to understand consumer buying behavior, preferences, and price sensitivity.
- Set prices aligned with local income levels, neighborhood demographics, and prevailing market competition.
- Analyze competitor pricing to maintain a balanced price-value position.
- Include introductory offers, combo deals, and seasonal pricing strategies.
Recruitment Strategy
Hiring the right team is essential for seamless supermarket operations.
Key Points
- Identify the number of employees required based on your store size, departments, and expected customer footfall.
- Prepare clear job descriptions for roles such as cashiers, floor staff, supervisors, inventory managers, and cleaners.
- Build a robust recruitment plan to attract skilled, reliable, and customer-friendly candidates.
- Focus on hiring staff trained in customer service, inventory handling, and POS operations.
- Include training programs to ensure smooth store functioning and consistent service quality.
- Plan shift schedules and staffing patterns to cover peak hours and weekends efficiently.
Conclusion
Opening a supermarket in India requires strategic planning across legal, financial, and operational dimensions. The checklists outlined in this article will help aspiring entrepreneurs navigate the complexities of the supermarket retail ecosystem with confidence. To ensure customer satisfaction and maintain optimal productivity and efficiency, adopting modern technology, especially cloud-based supermarket software, is important. By following this comprehensive checklist and staying adaptable to evolving market trends, you can successfully establish a thriving supermarket business in India and contribute to the nation’s rapidly growing retail sector.
Using cloud-based supermarket software, ERP systems, and POS solutions ensures smooth operations, accurate inventory management, and enhanced customer satisfaction. By following this comprehensive checklist, entrepreneurs can establish a profitable and scalable FMCG supermarket business and succeed in India’s dynamic retail sector.
Call at +91-73411-41176 or send us an email at sales@logicerp.com to book a free demo for starting your supermarket retail business with the best retail POS system and supermarket ERP software today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the first step to start a supermarket in India?
The first step is to create a comprehensive business plan. Define the scale of your supermarket, capital requirements, product range, target customers, and growth strategy. Selecting the right location and ownership structure is also important.
2. What licenses are required to open a supermarket in India?
Key licenses include:
- Shop and Establishment License – for employee rights and safety.
- FSSAI License – mandatory for selling packaged or fresh food.
- GST Registration – required for businesses with turnover above ₹40 lakh (₹20 lakh in special states).
- Import Export Code (IEC) – if you plan to import/export products.
- Professional Tax (PT) – applicable in most states for employee salaries.
3. How much capital is required to start a supermarket in India?
Capital depends on the size and scale of your supermarket. Typical costs include property rent/purchase, interior design, shelving, initial stock, POS and ERP software, marketing, and staff salaries. Call at +91-73411-41176 or send us an email at sales@logicerp.com to know about supermarket prices, and details today!
4. Which software is essential for a supermarket?
- Supermarket ERP Software – for accounting, inventory management, multi-store operations, and CRM.
- Supermarket POS Software – for billing, GST compliance, and customer management.
- Inventory Management Software – to track stock levels, expiry dates, and reorder alerts.
5. How to choose the best location for a supermarket?
Select areas with high footfall, middle-to-high income residents, and minimal competition. Ensure the location has ample parking and storage, good visibility, and accessibility from main roads.
6. What products should I stock in my supermarket?
Essential categories include:
- Staples: Rice, wheat, flour, pulses, sugar.
- FMCG Products: Snacks, beverages, cleaning products, personal care.
- Fresh Produce: Fruits, vegetables, dairy, and meat (if permitted).
- Specialty Products: Organic, imported, or premium items.
7. How to market a supermarket in India?
Use a mix of offline and digital marketing: flyers, banners, newspaper ads, social media campaigns, WhatsApp promotions, loyalty programs, seasonal discounts, and grand opening events.
8. What is the role of SOPs in supermarket operations?
SOPs ensure smooth and consistent operations, covering inventory management, customer service, employee training, safety, cash handling, marketing, and technology use. Proper SOPs reduce errors and improve efficiency.
9. How to recruit staff for a supermarket?
Hire cashiers, store attendants, supervisors, and managers. Train them in POS and ERP software, inventory management, and customer service. Maintain structured shifts and performance monitoring.
10. Can I start a supermarket with multiple branches in India?
Yes. Multi-branch supermarkets should invest in centralized ERP software for synchronized billing, inventory, and reporting across locations. Ensure each branch complies with local licensing and GST regulations. Call at +91-73411-41176 or send us an email at sales@logicerp.com to book a free demo for supermarket multi-store ERP software today!