Garment Barcode: Types, Benefits, and Industry Best Practices

Discover how garment barcodes integrated with ERP software help garment manufacturers and retailers automate inventory, reduce errors, optimize supply chains etc.
Introduction
Garment barcodes have revolutionized the way clothing manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers manage inventory, track products, and deliver customer satisfaction. From unique product codes to enhanced supply chain tracking, the right barcode system can boost efficiency across every stage of the apparel business. With LOGIC ERP garment retail software, businesses can integrate advanced barcode solutions seamlessly into their processes.
In this article, let’s explore a complete guide to types of garment barcode, benefits and industry best practices to boost accuracy, efficiency, and traceability in garment businesses.
Table of Content
- What is a Garment Barcode?
- Types of Garment Barcodes
- Benefits of Using Barcodes in Garment Industry
- Different Types of Garment Barcode Labels
- How to Choose the Right Garment Barcode Solution
- Implementing Garment Barcodes in Your Business
- Challenges and Future Trends
- Conclusion
- Summary
- Key Takeaways
- FAQs About Garment Barcodes
What Is a Garment Barcode?
Understanding the garment barcode definition helps businesses grasp what is a barcode and how it powers a garment identification system for accurate product tracking.
-
Definition and Purpose
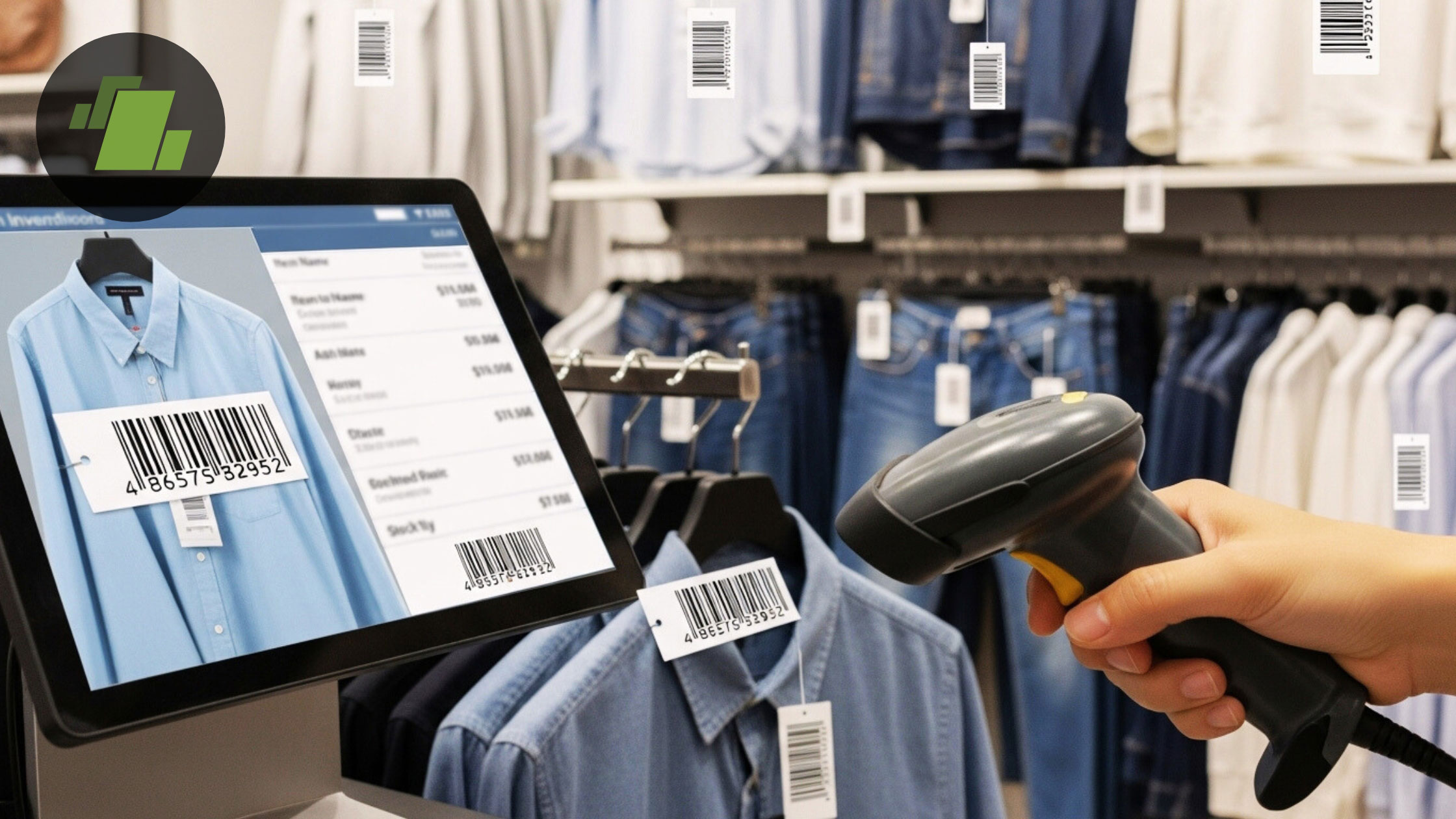
A garment barcode is a machine-readable optical label that contains essential product information encoded in a series of parallel lines or geometric patterns. These barcode labels serve as unique product identifiers, enabling automated data capture and seamless integration with inventory management systems, point of sale terminals, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions i.e. LOGIC ERP.
A barcode tag with a unique product code and woven barcode label helps ensure garment authentication and accurate tracking. Using a barcode printer, businesses can generate manufacturing barcodes and care label details for every barcode for garments.The primary purpose of garment barcodes is to create a digital bridge between physical garments and digital systems, facilitating real-time data exchange that enhances operational efficiency across the entire supply chain.
-
How Barcodes Are Used in the Garment Industry?
Barcode label printing software and free barcode generators have made it easier for small businesses to implement efficient barcode systems tailored to their needs. With access to garment barcode templates and apparel barcode solutions, retailers can follow garment barcode standards while enhancing inventory control and supply chain efficiency. Barcode scanning apps and barcode for retail stores support seamless operations across logistics, retail stores, and warehouses.
Using barcodes for traceability, brand protection, and anti-theft measures is now a garment industry best practice, ensuring both security and accuracy from production to point-of-sale. From initial manufacturing stages to final retail transactions, these codes enable:
1. Manufacturing Integration
Garment manufacturers use barcodes to track production batches, monitor quality control checkpoints, and manage work-in-progress inventory. When integrated with garment manufacturing software & ERP systems, barcodes provide real-time visibility into production schedules and resource allocation.
2. Supply Chain Visibility
Distributors and wholesalers rely on barcode scanning using barcode for inventory control and barcode for supply chain to manage warehouse operations, track shipments, and maintain accurate stock levels. This visibility using barcode for logistics for modern supply chain management and logistics optimization.
3. Retail Operations
At the retail level, clothing barcodes streamline checkout processes, enable accurate inventory counts, and support advanced analytics for sales forecasting and demand planning.
-
Information Encoded in Garment Barcodes
Barcodes for small businesses and large scale garment industries help streamline operations and improve inventory accuracy with minimal investment.Following garment barcode best practices ensures consistency, compliance, and smooth retail workflows.They also play an important role in brand protection and anti-theft, securing products throughout the supply chain. Advcanced garment barcodes include all information for product identification:
- Unique Product Code
- Size and Color Information
- Retail Price
- Manufacturing Date
- Batch or Lot Number
- Garment Type or Category
-
Product Code, Size, Price, Manufacturing Details
1. Unique Product Codes: Each garment receives a distinct identifier that differentiates it from all other products in the system. This code typically follows international standards like UPC or EAN formats.
2. Size and Variant Information: Barcodes can encode specific size information (S, M, L, XL) and color variants, enabling precise inventory tracking at the SKU level.
3. Pricing Data: While not always encoded directly in the barcode, the product code links to pricing information in connected systems, ensuring consistent pricing across all sales channels.
4. Manufacturing Metadata: Advanced implementations include batch numbers, production dates, quality control flags, and supplier information, creating a comprehensive digital trail for each garment.
Types of Garment Barcodes
Understanding the different barcode formats available helps businesses choose the most appropriate solution for their specific needs and operational requirements. Different types of barcodes, including UPC barcode, EAN barcode, Code 128, QR code, and manual barcode, follow international barcode standards to ensure each product has a unique barcode for global identification.

-
UPC (Universal Product Code)
Used primarily in North American retail, UPC barcodes consist of 12 numeric digits and are ideal for standardized inventory and POS systems.
-
Usage and Format
The Universal Product Code remains the most widely recognized barcode format in North American retail environments. UPC barcodes consist of 12 digits and are ideal for standardized retail products.
Format Structure: UPC-A barcodes contain a manufacturer code, product code, and check digit, providing a globally unique identifier for each product variant.
Best Applications: Perfect for retail-focused garment businesses that primarily serve North American markets or require compatibility with major retail chains.
-
EAN (European Article Number)
EAN-13 barcodes are globally recognized and ideal for international apparel exports. EAN barcodes contain 13 digits and work seamlessly with retail barcode scanning.
-
Global Applications
The European Article Number system offers broader international compatibility and is the preferred format for global garment brands and manufacturers.
International Standards: EAN-13 barcodes provide compatibility with international retail systems and are recognized worldwide, making them ideal for export-oriented businesses.
Scalability: The EAN system accommodates larger product catalogs and provides more flexibility for businesses with extensive product lines.
-
Code 128
Code 128 is a high-density barcode that can store alphanumeric data and is widely used in garment manufacturing and logistics.
-
High-Density Information Encoding
Code 128 offers superior data density and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring extensive product information encoding.
Variable Length: Unlike fixed-length UPC and EAN codes, Code 128 can encode variable amounts of alphanumeric data, perfect for complex product coding schemes.
Internal Operations: Particularly useful for internal inventory management, work-in-progress tracking, and integration with manufacturing execution systems.
- QR Codes
Two-dimensional barcodes that can hold much more information than traditional barcodes. Often used in marketing, warranty, and interactive experiences.
-
Marketing and Additional Information
Quick Response codes represent the next evolution in garment identification, offering enhanced functionality and customer engagement opportunities.
Enhanced Data Capacity: QR codes can store significantly more information than traditional linear barcodes, including URLs, care instructions, and brand storytelling content.
Consumer Interaction: Enable direct customer engagement through embedded links to product pages, care instructions, or authentication portals.
- Manual and Custom Barcodes
These are created for internal use or when dealing with non-standardized products. LOGIC ERP allows custom barcode generation.
-
When to Use Them
Certain scenarios require custom barcode implementations that don’t follow standard formats:
Prototype Management: During product development phases, custom codes help track samples and prototypes through design iterations.
Internal Process Control: Custom formats optimize specific internal workflows while maintaining compatibility with existing systems.
Benefits of Using Barcodes in Garment Industry
The implementation of quality barcode systems delivers measurable benefits across all aspects of garment business operations. Garment barcode benefits include enhanced inventory management, accurate stock control, and improved retail efficiency. They also increase speed at checkout, making operations smoother and more customer-friendly.
-
Improved Inventory Management
With garment barcode scanning in LOGIC ERP, inventory is updated in real-time, minimizing discrepancies and optimizing stock.
-
Real-Time Tracking and Stock Accuracy
Barcode implementation transforms inventory management from a manual, error-prone process into an automated, accurate system that provides real-time visibility.
Automated Stock Updates: Each scan automatically updates inventory levels across all connected systems, eliminating manual data entry and reducing human error.
Cycle Count Efficiency: Barcode scanning accelerates physical inventory counts, enabling more frequent stock verification and improved accuracy.
Integration Benefits: When connected to ERP systems like LOGIC ERP, barcode data provides comprehensive visibility into stock levels, reorder points, and demand patterns.
-
Faster Checkout Process
Barcoded garments processed at the POS ensure quicker customer checkouts and better service.
-
Reducing Queues and Human Error
Point of sale efficiency directly impacts customer satisfaction and operational costs. Barcode scanning dramatically improves checkout speed and accuracy.
Transaction Speed: Barcode scanning reduces average transaction time by 60-80% compared to manual price lookup and entry.
Error Reduction: Automated data capture eliminates pricing errors and ensures accurate tax calculations and inventory adjustments.
Staff Productivity: Reduced checkout times allow staff to focus on customer service and other value-added activities.
-
Enhanced Traceability
Each barcode offers insight into a garment’s lifecycle, from manufacturing to end-user delivery, ensuring complete transparency.
-
From Manufacturer to Retailer
Complete supply chain traceability has become essential for quality control, compliance, and brand protection initiatives.
Origin Tracking: Barcodes enable complete product genealogy tracking from raw materials through manufacturing to final sale.
Quality Assurance: Rapid identification and isolation of quality issues prevent widespread problems and support efficient recall processes.
Compliance Support: Detailed tracking records support regulatory compliance and audit requirements across different markets.
-
Brand Authentication and Anti-Theft
Barcodes serve as an anti-counterfeit mechanism. LOGIC ERP ensures only verified SKUs pass through retail points.
-
Preventing Counterfeits and Loss
Advanced barcode implementations provide sophisticated brand protection and loss prevention capabilities.
Authentication Features: Specialized barcode formats and verification systems help customers and retailers identify genuine products.
Theft Prevention: Integration with security systems enables automated alerts and tracking of suspicious activities.
Gray Market Control: Unique regional coding helps brands monitor and control product distribution across different markets.
Different Types of Garment Barcode Labels
The physical implementation of barcode systems requires careful consideration of label types, materials, and application methods to ensure optimal performance and durability.

-
Hang Tags
Printed hang tags contain garment barcodes for branding and pricing. Used in retail packaging.
-
Branding and Pricing
Hang tag barcodes serve dual purposes, combining essential product information with brand presentation and customer communication.
Design Integration: Modern hang tags seamlessly integrate barcode functionality with brand aesthetics and marketing messages.
Information Density: Beyond basic product codes, hang tags can include size charts, care instructions, and promotional information.
Material Options: Available in various materials from cost-effective paper to premium cardstock, depending on brand positioning and durability requirements.
-
Woven Labels
Durable labels integrated into the garment. Suitable for luxury or high-end brands.
-
Durability and Aesthetics
Woven barcode labels provide permanent product identification that maintains readability throughout the garment’s lifecycle.
Wash Durability: High-quality woven labels withstand multiple wash cycles while maintaining barcode readability.
Brand Integration: Woven labels can incorporate brand logos, care symbols, and barcode information in a cohesive design.
Premium Applications: Ideal for high-end garments where label quality reflects overall product quality and brand positioning.
-
Printed Labels
Cost-effective, flexible, and commonly used for fast fashion. Can be generated via barcode printing software.
-
Cost-Effectiveness and Flexibility
Printed barcode labels offer maximum flexibility and cost-effectiveness for high-volume applications and rapid product changes.
Variable Data: Digital printing enables unique barcodes and variable information on each label without setup costs.
Material Variety: Available on various substrates including taffeta, satin, polyester, and specialty materials for specific applications.
Quick Turnaround: Digital printing processes support rapid prototyping and short production runs.
-
Adhesive Stickers
Ideal for temporary labeling or packaging. Easy to print and apply.
-
Easy Application and Removal
Adhesive barcode stickers provide flexible solutions for temporary identification or post-production labeling requirements.
Application Versatility: Can be applied to garments, packaging, or temporary tags depending on operational needs.
Removability Options: Available with permanent or removable adhesives to support different business processes.
Cost Efficiency: Most economical option for basic barcode requirements and temporary applications.
-
Care and Size Labels
These labels contain washing instructions, material composition, and size details — integrated with barcode for compliance.
-
Compliance and Customer Information
Specialized labels combine regulatory compliance requirements with barcode functionality for comprehensive product information.
Regulatory Compliance: Meet legal requirements for care instructions while providing barcode functionality.
Space Optimization: Efficiently utilize limited label space for multiple information requirements.
Customer Value: Provide essential care information while enabling easy returns and inventory management.
How to Choose the Right Garment Barcode Solution
Selecting the optimal barcode solution requires careful evaluation of multiple factors including operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term scalability needs.
-
Material Considerations
Material considerations like fabric compatibility, adhesive strength, and durability impact the effectiveness of garment barcode labels.
-
Polyester, Taffeta, Satin, Paper
Material selection directly impacts barcode durability, readability, and overall cost-effectiveness:
Polyester Labels: Offer excellent durability and chemical resistance, ideal for garments requiring frequent washing or exposure to harsh conditions.
Taffeta Applications: Provide smooth printing surfaces and professional appearance while maintaining cost-effectiveness for mid-range applications.
Satin Finishes: Deliver premium aesthetics for high-end garments while supporting high-resolution barcode printing.
Paper Solutions: Most economical option for temporary applications or cost-sensitive products where durability is not critical.
-
Size and Design
Labels should match garment type and brand aesthetics. LOGIC ERP provides garment barcode templates for easy selection.
-
Matching Garment Requirements
Barcode size and design must balance readability requirements with aesthetic considerations and space constraints.
Scanning Distance: Larger barcodes support scanning from greater distances but require more space on the garment or packaging.
Aesthetic Integration: Design considerations ensure barcodes complement rather than detract from product presentation.
Space Constraints: Optimize barcode dimensions for available space while maintaining scanning reliability.
-
Printing Methods
Barcode printing methods must align with label material, garment handling conditions, and scanner compatibility.
-
Thermal Transfer, Direct Thermal, Digital
Different printing technologies offer varying advantages for specific applications and volume requirements.
Thermal Transfer Printing: Provides excellent durability and print quality for high-volume applications requiring long-term readability.
Direct Thermal Solutions: Offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness for temporary applications or short-term identification needs.
Digital Printing: Enables variable data printing and small batch production with excellent flexibility and quality.
-
Customization Options
From label size to fabric type, customization options ensure barcodes align with your garment specifications and retail requirements.
- Brand Logos, Additional Text
Modern barcode labels can incorporate extensive customization while maintaining scanning functionality.
Brand Integration: Seamlessly incorporate company logos, brand colors, and design elements without compromising barcode performance.
Additional Information: Include supplementary text such as washing instructions, size information, or promotional messages.
Multi-Language Support: Accommodate international markets with multi-language labels and region-specific information.
-
Selecting a Manufacturer
Choosing the right manufacturer ensures your barcode labels meet industry standards and withstand handling, washing, and retail conditions.
- Quality, Support, Lead Time
Choosing the right barcode label manufacturer impacts long-term success and operational efficiency.
Quality Standards: Evaluate printing quality, adhesive performance, and material durability through sample testing and references.
Technical Support: Ensure manufacturers provide comprehensive support for implementation, troubleshooting, and ongoing optimization.
Production Capacity: Verify ability to meet volume requirements and delivery schedules, especially during peak seasons.
Integration Expertise: Seek manufacturers with experience in ERP integration and industry-specific requirements.
Implementing Garment Barcodes in Your Business
Successful barcode implementation requires systematic planning, careful integration, and comprehensive staff training to maximize benefits and minimize disruption.
-
Integrating with POS Systems
LOGIC ERP offers built-in POS modules that sync with barcode scanners and printers.
-
Ensuring Compatibility
Effective barcode implementation begins with seamless POS integration, ensuring compatibility with system requirements and operational processes. Testing barcodes guarantees they’re compatible with POS systems and inventory tools.
System Compatibility: Verify barcode formats are supported by existing POS hardware and software systems before implementation.
Database Integration: Ensure product information flows seamlessly between barcode systems, inventory management, and sales reporting.
ERP Connectivity: For businesses using comprehensive systems like Logic ERP, verify seamless data exchange between barcode scanning and enterprise-wide business processes.
Testing Protocols: Conduct thorough testing of all system integrations before full deployment to identify and resolve potential issues.
-
Standardizing Barcode Formats
Support for UPC, EAN, and Code 128 ensures compatibility with global garment retailers.
-
UPC, EAN, Code 128
Format standardization across all products and locations ensures consistent operations and reduces complexity.
Format Selection: Choose primary barcode format based on market requirements, international presence, and system compatibility needs.
Consistency Requirements: Maintain consistent format usage across all product lines, locations, and business processes.
Migration Planning: For businesses transitioning between formats, develop comprehensive migration plans that minimize operational disruption.
Documentation Standards: Create clear documentation of barcode standards and formats for staff training and vendor coordination.
-
Testing for Readability
Ensure printed barcodes are scannable under different lighting conditions and environments. Use barcode scanning apps for quality checks.
-
Before Mass Production
Comprehensive testing prevents costly production issues and ensures reliable barcode performance across all operational environments.
Print Quality Verification: Test barcode print quality across different materials, printing methods, and environmental conditions.
Scanner Compatibility: Verify readability across all scanning devices used in operations, including handheld scanners, fixed scanners, and mobile applications.
Environmental Testing: Evaluate barcode performance under realistic conditions including lighting, temperature, and handling scenarios.
Durability Assessment: Test barcode longevity through simulated wear, washing, and aging processes relevant to product lifecycle.
-
Training Staff
Train warehouse and retail staff on barcode scanning, POS usage, and garment tracking through Logic’s onboarding programs.
-
Effective Use and Troubleshooting
Comprehensive staff training ensures successful adoption and maximizes return on barcode investment.
Operational Training: Provide hands-on training for all staff involved in barcode scanning, from warehouse operations to retail checkout.
Troubleshooting Skills: Develop staff capabilities to identify and resolve common barcode scanning issues independently.
System Integration: Train staff on how barcode scanning integrates with broader business processes and ERP systems.
Continuous Education: Establish ongoing training programs to address system updates, new features, and operational improvements.
Challenges and Future Trends
Understanding current challenges and emerging trends helps businesses make informed decisions about barcode technology investments and implementation strategies.
-
Common Implementation Challenges
Implementing garment barcodes can face challenges like system integration issues, data inaccuracies, and staff training gaps.
Overcoming these requires proper planning, reliable software solutions, and support from experienced ERP partners.
-
Cost, Compatibility, Privacy
Despite significant benefits, barcode implementation presents several challenges that require careful planning and management.
Initial Investment: Barcode system implementation requires upfront investment in hardware, software, training, and process redesign that may strain budgets.
Legacy System Integration: Older systems may require significant modification or replacement to support modern barcode functionality effectively.
Data Privacy Concerns: Increased data collection capabilities raise privacy considerations that must be addressed through appropriate policies and security measures.
Change Management: Staff resistance to new processes and technologies can impede successful implementation without proper change management strategies.
-
The Rise of RFID
RFID technology is rapidly transforming the garment industry by enabling real-time tracking, faster checkouts, and enhanced inventory accuracy.
Unlike traditional barcodes, RFID tags offer greater data capacity and can be scanned without direct line of sight, boosting efficiency across the supply chain.
- Advantages Over Traditional Barcodes
Radio Frequency Identification technology represents the next evolution in product tracking and identification systems.
Bulk Scanning: RFID enables simultaneous reading of multiple items without line-of-sight requirements, dramatically improving inventory efficiency.
Enhanced Data Storage: RFID tags can store significantly more information than traditional barcodes and support real-time data updates.
Automated Processes: RFID enables fully automated inventory tracking and management with minimal human intervention.
Integration Potential: Advanced RFID systems can integrate seamlessly with existing ERP platforms like Logic ERP for comprehensive business intelligence.
-
Sustainability and Efficiency
By minimizing waste and improving tracking, garment barcodes promote sustainable inventory management. They help reduce overproduction, returns, and resource consumption in apparel operations.
-
Reducing Waste, Improving Logistics
Environmental considerations increasingly influence barcode technology selection and implementation strategies.
Eco-Friendly Materials: Growing availability of biodegradable and recyclable barcode label materials supports sustainability initiatives.
Digital Integration: Enhanced digital connectivity reduces paper-based processes and supports paperless operations.
Supply Chain Optimization: Improved tracking and visibility enable more efficient logistics and reduced environmental impact through optimized transportation and inventory management.
Waste Reduction: Better inventory accuracy and demand forecasting reduce overproduction and waste throughout the supply chain.
FAQs About Garment Barcodes
Our garment barcode FAQ covers common questions, barcode troubleshooting tips, and best practices for smooth implementation. Explore free barcode software and barcode generators to create accurate labels tailored to your apparel business needs.
What information does a garment barcode contain?
Garment barcodes typically contain a unique product identifier that links to comprehensive product information stored in connected databases. This can include product name, SKU, size, color, price, manufacturer details, and inventory status. Advanced implementations may also encode batch numbers, production dates, and quality control information directly in the barcode.
How do I generate a barcode for my garments?
Barcode generation requires specialized software that converts product information into scannable formats. LOGIC ERP includes integrated barcode generation capabilities. Alternatively, dedicated barcode software or online barcode generators can create codes in various formats. The key is ensuring your chosen method produces industry-standard codes compatible with your scanning equipment and business systems.
Which barcode type is best for my business?
The optimal barcode type depends on your specific business requirements. UPC codes work best for North American retail focus, while EAN codes provide international compatibility. Code 128 offers flexibility for internal operations and variable data encoding. QR codes enable enhanced customer engagement and information storage. Consider your target markets, scanning requirements, and data needs when making this decision for barcode for traceability.
How do I ensure my barcodes are scannable?
Scannable barcodes require attention to print quality, size specifications, and environmental factors. Maintain adequate contrast between bars and background, ensure minimum size requirements are met, and test across all scanning devices in your operations. Regular quality checks during production and proper storage of barcode labels help maintain scanning reliability throughout the product lifecycle.
Can I print barcode labels in-house?
In-house barcode printing is possible with appropriate equipment and software. Thermal transfer and direct thermal printers offer good quality for most applications, while digital printers provide flexibility for variable data and short runs. Consider volume requirements, quality needs, and total cost of ownership when deciding between in-house printing and outsourcing to specialized manufacturers.
Conclusion
-
Recap of Key Benefits
Garment barcodes are a powerful tool for modern apparel businesses, improving inventory accuracy, streamlining operations, and enhancing customer experiences. When integrated with LOGIC ERP, they enable seamless data flow across departments. This real-time visibility helps businesses make faster decisions, improve forecasting, and deliver better service.
-
Steps to Get Started
In order to get started with barcode scanning apps, and apparel barcode solutions, assess your current systems, choose the right barcode formats, and work with reliable label vendors. Test thoroughly, train your staff, and partner with ERP experts for smooth integration and efficient execution.
-
Where to Find Expert Help for Barcode Software?
Need help implementing barcode systems for your garment business? Contact LOGIC ERP for end-to-end barcode solutions – including software, hardware integration, and expert consultation.
For next steps and expert guidance, contact us for tailored barcode solutions that fit your apparel operations. Contact for barcode solutions by calling at +91-73411-41176 or send us an email at sales@logicerp.com today. Book a free demo and get the best apparel barcode solutions today!
Garment Barcode Summary
Unlock detailed information of garment barcodes with this complete guide, covering types, benefits, and industry best practices to boost accuracy and efficiency. Discover how integrating with ERP systems can transform your apparel business with smarter, faster, and scalable operations.
Key Takeaways
- Garment barcodes play a vital role in inventory accuracy, stock control, and retail efficiency.
- Different types of barcodes like UPC, EAN, Code 128, and QR codes serve specific garment industry needs.
- Barcode systems improve speed at checkout, product traceability, and supply chain visibility.
- Integration with LOGIC ERP enhances real-time data flow and operational control.
- Following garment barcode best practices ensures durability, readability, and compliance with industry standards.
- Proper testing, POS integration, and staff training are essential for successful implementation.
- Barcode label customization, material selection, and printing methods affect performance and longevity.
- Barcodes support brand protection, anti-theft measures, and garment authentication.
- RFID is emerging as a powerful complement to traditional barcode technology.