A Step-By-Step Guide to Implementing Supermarket Billing & ERP Software
Introduction
Supermarkets run on speed, accuracy, visibility, and tight margins. Even the smallest inefficiency, slow billing, stock mismatches, expired goods, or manual bookkeeping can impact customer experience and profitability. That’s why supermarket billing software and supermarket ERP software have become the backbone of modern retail stores.
But successful implementation does not happen automatically. It requires a structured, strategic, and step-by-step approach. Implementing a robust Supermarket Billing & ERP Software transforms operations, speeding up billing, automating inventory and accounting, ensuring compliance, reducing waste, enabling data-driven decisions, and more.
This guide will walk you through a step-by-step, end-to-end process for implementing such a system from initial planning to rollout, and beyond. It’s structured to help supermarket owners, store managers, or retail chain operators (single or multi-store) achieve a smooth, scalable implementation.
Why Supermarkets Need Integrated Billing & ERP Software
Before diving into steps, it’s important to understand why modern supermarkets benefit enormously from integrated billing + ERP systems:
- Faster, Accurate Billing and Checkout
Barcode scanning, POS integration, weighing-scale support, and automatic price & discount calculation reduce queues, speed up checkout, and eliminate human errors.
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking & Stock Control
Every sale, return, or stock movement updates inventory instantly. This prevents stockouts, overstocking, spoilage, and losses due to expired or unsold goods.
- GST / Tax Compliance & Accounting Integration
A billing system integrated with accounting and GST/e-invoice modules ensures compliant invoices, accurate tax filing, and reduced manual accounting errors.
- Centralized Control for Multi-Store or Chain Operations
For businesses with multiple outlets, centralized ERP supports uniform pricing, inventory tracking, promotions, and aggregated reporting.
- Business Intelligence, Analytics & Reporting
With digital data capture, dashboards reveal sales trends, best-selling items, slow-moving stock, seasonal demand, margins, and profitability insights for better decision-making.
- Improved Customer Loyalty and Experience
Loyalty programs, discounts, CRM tools, and faster checkout create better customer experiences and increase customer retention.
- Efficiency, Cost Savings, Waste Reduction & Scalability
Automating repetitive tasks reduces labor costs, errors, and stock losses. Cloud-based ERP solutions scale easily with business growth and expansion.
Given these advantages, implementing supermarket billing + ERP systems is essential for retailers aiming for efficiency, accuracy, and growth.
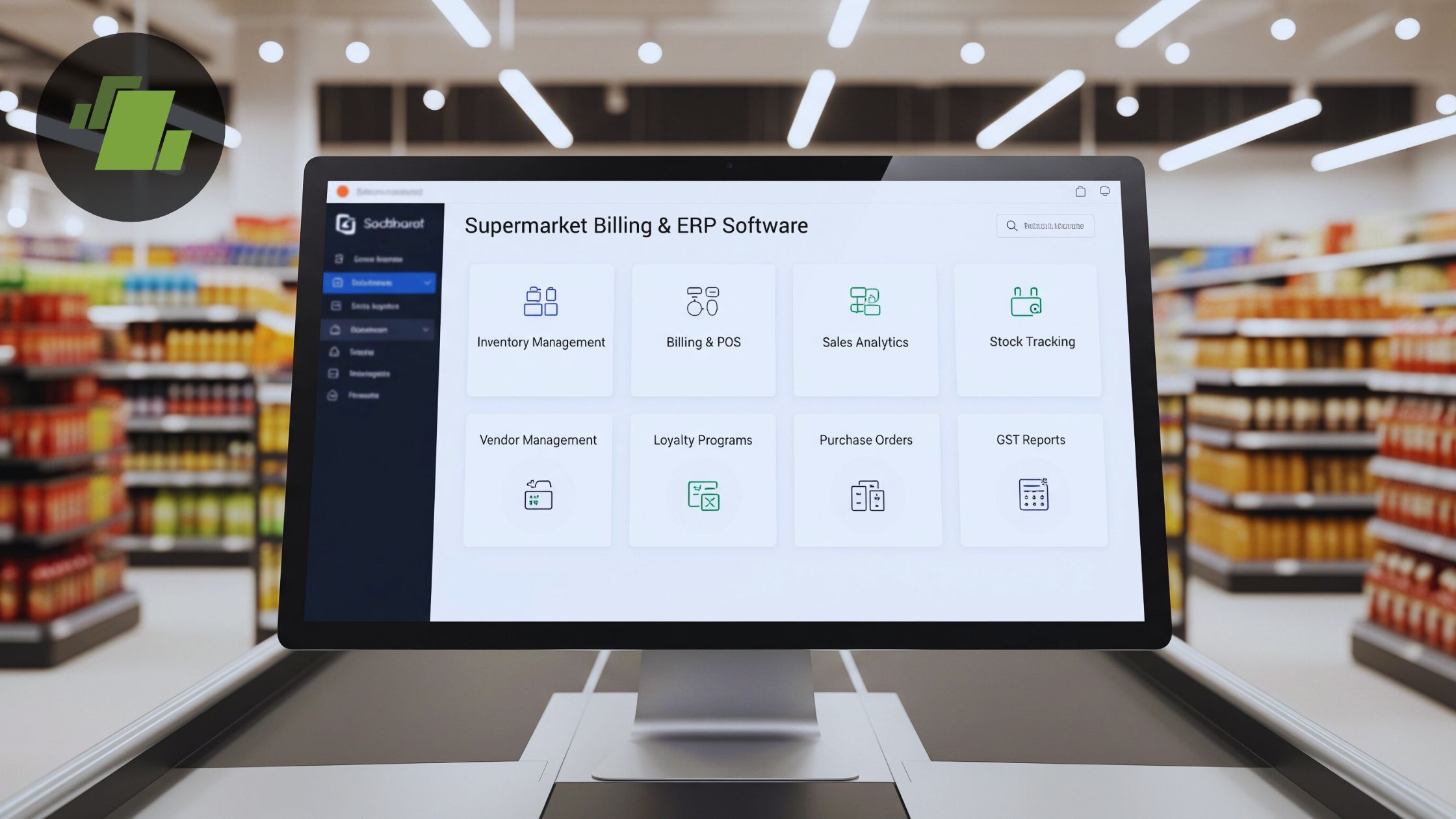
Key Features & Requirements Before You Start
Before selecting or implementing software, it’s critical to know what features your supermarket really needs. The “right” software should support:
- Real-time inventory management (stock levels, batch/lot tracking, expiry management, perishable tracking)
- Integrated Point of Sale (POS) / Billing module : Barcode scanning, weighing scale integration (for items sold by weight), multiple payment modes (cash, card, UPI, wallets), discount & offer management, loyalty programs, GST & tax calculation, invoice printing/email/e-invoice support.
- Centralized accounting & tax compliance : Ledger, accounts payable/receivable, GST/HSN/SAC, e-way bills, financial reporting.
- Multi-store / multi-branch support (if you have more than one outlet) : Centralized control of inventory, pricing, promotions, stock transfer, consolidated reporting.
- Analytics & Business Intelligence : Dashboards showing sales trends, best and slow-moving products, profitability, demand forecasting, reorder alerts.
- User roles and access control : Restrict access based on role (cashier, manager, admin), audit trails, secure data handling.
- Scalability, cloud or on-premise deployment, backup & data security to support growth, avoid data loss, and allow remote access.
- Flexibility for promotions/discounts, loyalty programs, supplier management, purchase orders, vendor management to support procurement and customer retention strategies.
Pre-implementation checklist | Things to decide/prepare up front:
- Do you need single-store or multi-store support?
- Will you sell perishable goods that require batch/expiry tracking?
- Do you need integrated weighing scales / barcode scanners / card machines / UPI etc.?
- Are you required to comply with GST / e-invoicing / e-way bill regulations (especially relevant for India)?
- Do you have processes for purchase orders, supplier management, returns/expiry, stock transfers, etc.?
- Do you need customer loyalty, promotions, CRM modules?
- What reporting/analytics do you need : daily sales, inventory turnover, margins, waste tracking, etc.?
- Hardware & network readiness (POS terminals, printers, UPS, stable internet for cloud or on-premise backups)
Having clarity on these requirements helps you choose the right software and plan implementation more smoothly.
Step 1: Pre-Implementation: Planning & Preparation
Starting implementation without planning is risky. Here’s how to prepare effectively:
1. Define Your Goals & Scope
- Are you replacing the manual/billing-only system, or replacing an old POS?
- Are you implementing only in one store, or multiple stores / branches?
- Do you want basic billing + inventory, or full ERP (accounts, procurement, CRM)?
- What improvements do you expect : faster billing, reduced waste, better inventory, compliance, multi-store sync, analytics, etc.
2. Form a Project Team
Include stakeholders: store owner / manager + cashier heads + inventory manager + accountant/finance + IT support (if any) + vendor (software provider) liaison. Clear roles help smooth implementation.
3. Prepare Data | Inventory, Suppliers, Products
Make master lists of all products: SKUs, categories, HSN/HSN codes (for tax), prices, batches, expiry; suppliers, purchase history. This data will be migrated to ERP.
4. Procure Hardware & Infrastructure
POS terminals or tablets, barcode scanners, weighing scales (if required), bill printers, backup internet/UPS, network setup, racks, storage for stock etc.
5. Plan Timeline & Pilot Schedule
Implementation should ideally be phased: pilot → soft launch → full rollout. This reduces disruption to business and allows adjustments if issues arise.
6. Selecting the Right Billing & ERP Software
Choosing the right software is important. Here’s how to evaluate and select:
7. Create a Requirements Checklist
Based on the features and needs listed in Section 3, prepare a checklist. Use this when evaluating vendors.
8. Evaluate Popular Options | On-Premise vs Cloud
Some supermarkets prefer cloud-based ERP for easy remote access, backup, scalability; others may choose on-premise for data control or offline reliability. Evaluate pros & cons for your context.
9. Check for Retail-Specific Modules
Generic ERP may not cater to supermarket needs (barcode scanning, batch/expiry tracking, weighing scale integration, perishable goods, loyalty programs). Prefer ERP built for retail/supermarket.
10. Test Demo / Free Trial
Many vendors offer free trials or demos. Use them to test features: billing speed, inventory update, GST invoice generation, report generation, ease of use. This prevents surprises post go-live.
11. Assess Vendor Support, Training & Implementation Services
Good vendors offer setup support, training, user manuals, data migration help, and post-implementation support. Critical for smooth rollout.
12. Cost vs Value Analysis
Consider license/ subscription cost, hardware cost, training and support cost vs expected benefits: efficiency, reduced losses, better control, growth, scalability.
Once you pick the software, get ready for hardware setup and data preparation.
Step 2 :Hardware, Infrastructure & Setup
With software chosen, now set up the hardware and infrastructure:
- POS Terminals / Computers / Tablets: For billing counters should support barcode scanner, weighing scale, printer, payment terminals.
- Barcode Scanners & Weighing Scales: Essential for fast billing, especially for supermarkets selling weighed items. Integration must be supported by your software.
- Bill / Invoice Printers & Displays: For printing receipts/invoices and showing customers their items/prices.
- Stable Internet & Network Setup (if cloud-based): For real-time sync, backups, multi-store data sync. Consider backup internet or offline mode.
- Storage, Racks & Inventory Layout Planning: Decide physical storage, rack allocation (especially for perishable goods), batch/expiry labelling.
- Staff Workstations & Access Control Setup: Different user roles: cashier, store manager, inventory manager, admin with role-based permissions for data security.
Proper hardware and setup ensures the software can function at full capacity.
Step 3: Data Migration & Master Setup
One of the most important and often overlooked steps is data migration and master setup. Errors here can cascade into bigger problems later.
Prepare Master Data Files
List out all products/SKUs with: product code or barcode, description, category, HSN code (for GST), unit price, MRP, purchase price, sales price, tax rate, batch/lot number (if perishable), expiry date (if applicable), supplier details.
Suppliers & Purchase History
Create a vendor/supplier master list with contact info, credit terms (if any), past purchase history (if migrating), vendor codes.
Customer Data (if loyalty / credit accounts)
If you’re using loyalty programs or credit sales, prepare a customer master list: customer name, contact, loyalty ID, credit limits etc.
Import Data, or Manual Entry & Verification
Use vendor-provided import tools (often via CSV / Excel template) to upload master data. After import, run validation: check inventory count vs physical stock, ensure barcodes scan correctly, tax rates correct, product groups accurate, pricing right.
Audit & Reconcile
Do a stock and price audit after data migration, count physical stock, match with system stock, correct mismatches, verify expiry/batch data, ensure GST settings are correct.
This master setup ensures that billing, inventory, and accounting work correctly from day one.
Step 4: Configuring Inventory, Billing, GST, and Other Modules
With data in place, configure the key modules:
Inventory Settings
- Define categories, units (piece, kg, litre), batch/expiry management (especially for perishables)
- Set reorder thresholds / low-stock alerts
- Enable batch / lot & expiry-date tracking if required
- If multiple warehouses / branches are there, configure warehouse structure, stock transfer rules
Billing Module Setup
- Configure payment modes (cash, card, UPI, wallet etc.)
- Barcode scanning & weighing scale integration (if selling items by weight)
- Discount and offer rules (item discount, bill discount, combo offers, loyalty discounts)
- GST / tax settings : HSN/SAC codes, tax slabs, GST rates for each product category, automatic tax calculation, e-invoice/e-way bill settings (if required)
- Invoice format: Define layout, what details to show (store name, GSTIN, item list, price, tax, total, barcode, loyalty points etc.)
Accounting & Finance Settings
- Configure ledger accounts, chart of accounts : sales, purchases, inventory, tax, expense, cash/bank, etc.
- Integrate POS transactions to accounting module so billing reflects in books automatically
- Set up vendor accounts, purchase orders, credit/ debit notes, returns, vendor payments, expense tracking
User Roles & Access Control
Define roles for cashier, manager, inventory manager, admin and assign permissions accordingly. Restrict sensitive operations (price change, discount override, stock adjustments) to authorized roles.
Reporting & Dashboard Configuration
Set up dashboards and periodic reports: daily sales, inventory stock levels, low-stock alert reports, expiry/near-expiry reports, slow-moving stock, profitability reports to enable data-driven decisions.
Once configurations are done, you are ready to test the system — but before full launch, run a pilot.
Staff Training and Change Management
Technology alone doesn’t succeed, people do. A big challenge in ERP adoption is user acceptance.
Step 5: Identify Key Users for Each Role
Cashiers, store manager, inventory manager, procurement, accountant, each should know their part.
Conduct Hands-On Training Sessions
- How to bill items : barcode scan, weigh, apply discounts, accept various payment modes
- How to handle returns, cancellations, partial payments, loyalty redemptions
- Inventory receiving, stock update, batch/expiry tracking, reorder alerts
- Purchase order creation & vendor payment processing
- Reporting : how to view dashboards, generate reports, interpret them
Provide Written SOPs & User Manuals
Document standard operating procedures (SOPs): billing flow, stock receiving, expiry check, discount application, stock transfer, backups, user-role responsibilities.
Communicate Benefits to Staff & Stakeholders
Explain how the new system will reduce manual workload, reduce billing errors, simplify tasks, and make stock management easier, creating buy-in.
Run Mock Transactions as Practice
Before going live, run test scenarios: large billing, multiple payment modes, returns, expiry goods, stock transfer, vendor purchase orders, reports to ensure staff familiarity and system stability.
Proper training reduces resistance, errors, and ensures smooth adoption.
Step 6: Pilot Run & Soft Launch
Rather than switching completely immediately, run a pilot phase / soft launch, to minimize business disruption.
- Choose a time when customer footfall is moderate (not peak).
- Use the system for real billing for a limited period, maybe one day or one week while simultaneously running manual fallback (if possible) to compare.
- Test all flows: billing, returns, discounts, payments, inventory update, stock receipt, expiry tracking, reports.
- Gather feedback from cashiers, store staff. Note hiccups, performance issues, user feedback.
- Fix configuration issues: wrong tax settings, barcode problems, hardware glitches, network or printing problems, discount rules mis-applied.
Pilot run helps you refine setup, address problems, and make adjustments before full rollout important for success.
Step 7: Full Rollout and Going Live
Once the pilot is successful and issues fixed, you can go live across the store (or all stores).
- Remove fallback/legacy systems. Rely solely on the new ERP for billing, inventory, etc.
- Monitor closely the first few days, watch for billing speed, checkout queues, inventory update accuracy, GST invoice correctness, payment processing, printouts.
- Ensure staff follow SOPs (billing flow, stock update, expiry logs, purchase orders).
- Communicate to customers (if needed), e.g., mention faster billing, better inventory, new loyalty/discount offers, to build goodwill.
Step 8: Monitoring, Reporting & Business Intelligence
Implementation is just the start. Long-term gains come from continuous monitoring, analysis, and optimization.
Daily / Weekly / Monthly Reports
- Daily sales summary, cashier-wise sales, best-selling products, low-stock alerts, expiry items report
- Stock turnover, slow-moving SKU reports, wastage or expiry losses, purchase order tracking, vendor returns or damages
Inventory Reordering & Procurement Planning
Use stock-level and sales trends to schedule automated reorders, purchase just-in-time, avoid overstocking or stockouts, especially for perishable goods.
Pricing, Promotions & Loyalty Programs
Use data on customer behaviour, purchase history, slow-moving items to design targeted promotions or discounts, clearing old stock, boosting sale of slow-moving goods, or offering loyalty incentives.
Financial & GST Compliance Reports
Use integrated accounting and GST modules to generate accurate tax reports, e-invoice/e-way bills if needed, reconcile ledgers, manage cash flow, and prepare for audits or returns filing.
Performance Review & Continuous Improvement
Review KPIs: billing speed, checkout time, customer wait time, stock turnover ratio, wastage rate, profitability per SKU/category, shrinkage, staff performance, use insights to optimize operations, staffing, reorder cycles, space planning.
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
Implementing ERP in retail/supermarkets comes with challenges. Here are common pitfalls & mitigation strategies:
| Pitfall | How to Avoid / Mitigate |
|---|---|
| Poor data migration (wrong SKU codes, mismatched stock counts, incorrect GST/tax codes) | Do thorough master data preparation and validation; run audits; reconcile physical stock with system data before going live. |
| Lack of staff buy-in / resistance to change | Provide adequate training, document SOPs, explain benefits, run pilots, involve staff in testing and feedback. |
| Hardware & infrastructure issues (slow POS, barcode scanner glitches, network downtime) | Procure reliable hardware, have backups (UPS, offline mode, redundant internet), test equipment thoroughly before live. |
| Incorrect configuration of billing/tax/discount rules | Test billing flows intensively (regular, discounts, returns) in pilot runs; verify invoices and tax calculations; audit financial entries. |
| Ignoring inventory best practices (expiry, batch management, FIFO/FEFO) | Enable batch/expiry modules; audit stock regularly; train staff to manage expiry-date tracking; set reorder/alert thresholds. |
| Over-reliance on software without SOPs | Document standard operating procedures, assign roles, enforce discipline for stock updates, returns, wastage handling, and audits. |
| Scaling without planning (sudden expansion, new branches) | Implement a scalable software; define processes for multi-store stocking, stock transfer, consolidated reporting, centralised procurement. |
Avoiding these pitfalls can significantly improve your success rate and ensure the ERP delivers expected benefits.
Scaling & Multi-Store / Chain Management (if you expand)
If you plan to grow, open new branches or expand to chain stores, integrated ERP software becomes even more valuable.
- Centralized inventory, pricing, promotions control: Manage stock across stores; transfer stock between branches; maintain uniform pricing & discounts.
- Consolidated reporting & analytics: View combined sales, profitability, inventory across all outlets; identify best performing stores, underperforming ones, stock trends.
- Unified supplier / purchase order management: Centralized procurement, better vendor negotiating power, bulk orders, standardized supply across stores.
- Consistent customer loyalty programs across stores: Unified loyalty database, cross-store redemption, better customer retention.
- Scalable infrastructure (cloud-based ERP, multi-branch support, remote access): Manage from headquarters; monitor stores remotely; deploy updates centrally.
Scaling with a modern ERP makes expansion manageable, maintainable, and efficient.
Post-Implementation Maintenance & Optimization
Implementation isn’t a one-time job. To ensure your supermarket reaps long-term benefits, you must maintain and optimize the system:
- Regular stock audits periodically reconcile physical stock vs system stock, especially for perishables/expiry, returns, damages.
- Update product master & pricing data, new SKUs, new products, seasonal items, price changes, tax updates.
- Backup and data security ensure regular backups (cloud or offline), secure access, update software/patches, audit logs.
- Staff refresher training is mandatory for adding every new module (e.g. loyalty, promotions, new payment mode), or staff turnover.
- Use sales and inventory data to run timely promotions, optimize procurement, manage stock, avoid wastage, plan for demand spikes (festivals, season, holidays).
- Iterate on processes & SOPs as the store evolves, customer behaviour changes, product range grows, adapt processes and SOPs.
Conclusion
Implementing supermarket billing & ERP software can streamline your retail business and drive growth. When done right with careful planning, proper software selection, correct setup, staff training, and continuous monitoring, such a system delivers huge benefits: faster billing, accurate inventory management, reduced waste, compliance readiness, better customer experience, data-driven decision making, and scalability.
While the process requires effort, data preparation, hardware setup, staff training, the long-term gains far outweigh the costs. Call at +91-73411-41176 or send us an email at sales@logicerp.com to book a free demo for LOGIC ERP supermarket retail software implementation today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Can small supermarkets or kirana shops benefit from ERP billing software, or is it just for large supermarkets?
Yes, even small supermarkets benefit significantly. Modern supermarket POS/ERP solutions scale down to simpler operations: fast billing, inventory tracking, GST compliance, purchase orders, and avoid manual inventory tracking. As business grows, the system scales.
Q2. Is cloud-based supermarket ERP better than on-premise?
Cloud-based ERP offers advantages: remote access, easy backups, data security, multi-store sync, and automatic updates. But if internet connectivity is unreliable, on-premise or hybrid models may be better. Choose based on your context.
Q3. How much time does it take to implement a supermarket ERP system?
It varies with store size and complexity. For a small single-store supermarket with limited SKUs, master data setup + training can take 1–2 weeks. For larger stores / chains with multiple SKUs, warehouses, and modules (accounting, purchasing, CRM), implementation may take several weeks + pilot phase before full rollout.
Q4. What about GST, e-invoicing and compliance?
Choose ERP that supports GST, HSN/SAC, automatic tax calculation, and e-invoice / e-way bill (if applicable). Proper configuration ensures invoices are compliant and simplifies filing.
Q5. Will implementing ERP reduce my operational cost?
Yes, by automating billing, inventory, procurement, accounting, and reporting, you reduce manual work, errors, wastage, overstocking, and shrinkage. Over time, improved efficiency and data-driven decision making boost profitability.