Bank Reconciliation Statement – BRS Full Form, Format, Meaning & Examples
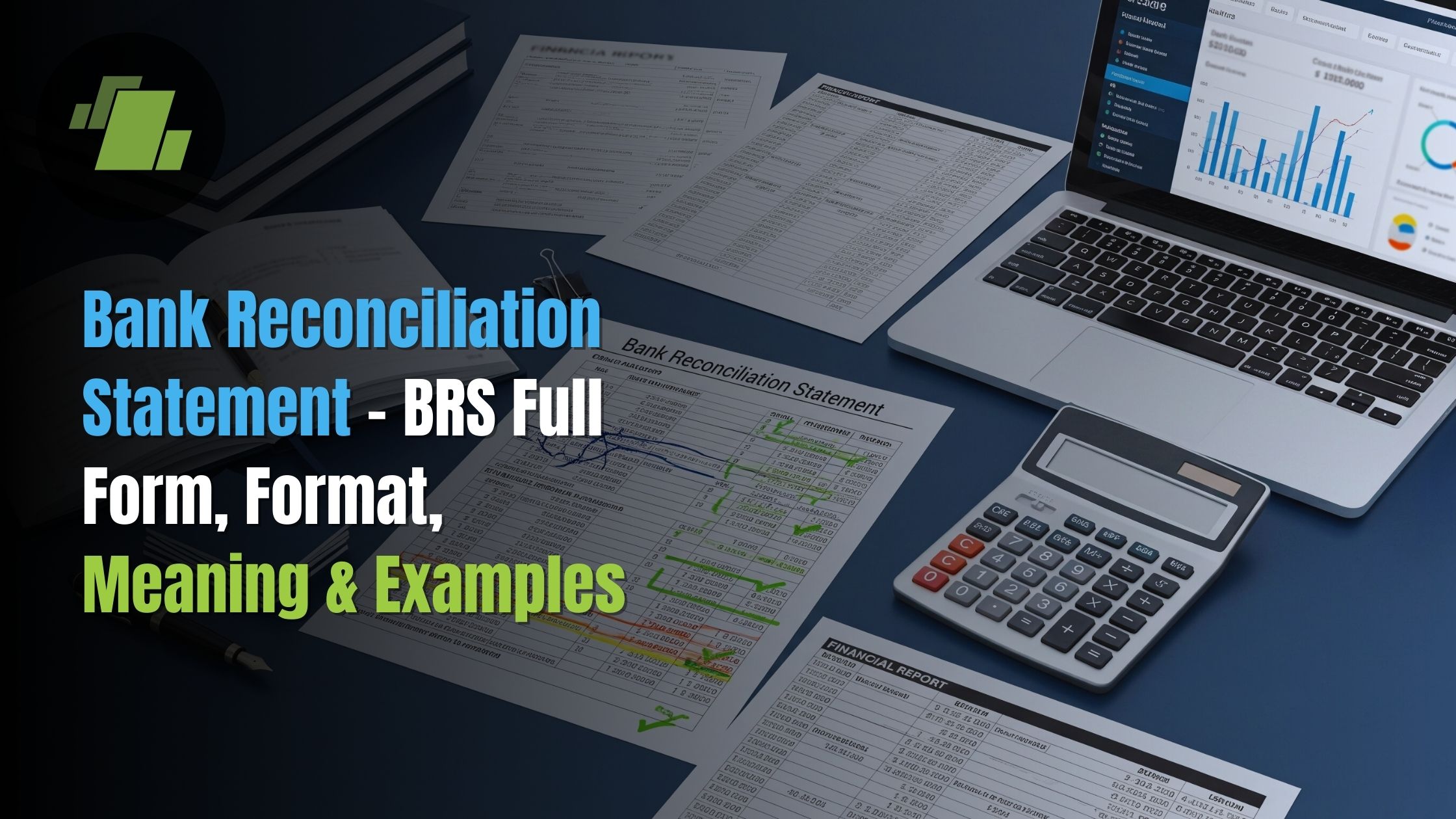
Have you ever wondered why your bank balance doesn’t always match your records? The Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) is here to reveal the hidden gaps.
What is BRS?
A Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) is the financial statement that helps businesses compare their own accounting records with the transactions recorded by the bank. Even if accounts are maintained carefully, differences often arise because of pending cheques, bank charges, deposits in transit, or interest adjustments. Preparing a BRS makes it easier to spot these mismatches, identify missing entries, and correct them on time.
What is the purpose of preparing it?
The BRS statement in accounting shows why the balance in your bank account (as per the bank) may not match the balance in your books.
It highlights pending transactions, bank charges, errors, or unrecorded deposits.
Bank Reconciliation Statement Format
The format of a BRS clearly shows reconciled and unreconciled items, giving businesses a transparent view of their finances. Companies usually prepare it on a daily, weekly, or periodic basis to keep their books accurate, reliable, and audit-ready.
The bank reconciliation statement (BRS) format makes it easy for businesses to compare their book balances with bank statements, either manually or through automated reconciliation. It clearly points out unreconciled items like pending cheques, bank charges, interest, or SMS transfers, so you can quickly find and fix any mismatches.
BRS helps businesses of all sizes manage cash flow better and keep their financial records reliable.
Importance of BRS
Mismatches in bank balances can be frustrating and time-consuming to track down. The Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) helps you quickly identify where and why these discrepancies occur. Some common situations include:
- Cheques issued but not presented: If a cheque you issued hasn’t been cleared by the bank or the receiver forgot to deposit it, it will appear as an unreconciled entry.
- Bank charges or interest: Since banks don’t always notify users about charges or credits via SMS, these often go unnoticed until reconciliation.
- Cheques deposited but not cleared: Incoming cheques often take time to clear. If these aren’t updated once cleared, they create mismatches in the books.
- Date mismatches: Differences between the cleared cheque date in your records and the actual bank date, common in post-dated cheques, can cause confusion and errors.
Advantages of Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)
1. Accurate Financial Records
2. Detection of Errors
3. Fraud Prevention
4. Improved Cash Management
5. Essential for Audits and Compliance
6. Timely Identification of Discrepancies
7. Transparency in Financial Operations
8. Supports Strategic Decision-Making
Step-by-Step: How to Prepare BRS
-
Login to LOGIC ERP
Open your ERP dashboard with valid credentials.
Navigate to the Accounts or Finance module.
-
Import Bank Statement
Upload your bank statement in the supported format (Excel, CSV, or direct bank integration if enabled).
The system automatically maps transactions with your ledger.
-
Match Transactions
LOGIC ERP helps to compare entries in the bank statement.
It highlights matched, unmatched, or pending transactions.
- Identify Discrepancies
Review differences such as:
Cheques issued but not cleared.
Deposits not yet credited.
Bank charges, interest, or penalties not recorded.
-
Adjust Entries
Pass adjustment entries directly from the BRS screen for unrecorded charges or transactions.
Update your ledger automatically.
- Generate BRS Report
Once all entries are reconciled, generate the Bank Reconciliation Statement.
LOGIC ERP provides a detailed report showing reconciled balance, pending items, and adjustments made.
- Save & Share
Export the final BRS in Excel/PDF format.
Share with management, auditors, or for compliance purposes.
Why Use Accounting Software for BRS?
- Automated Matching of Transactions
- Error-Free Reconciliation
- Time-Saving & Efficient
- Real-Time Financial Insights
- Audit-Ready Reports
Conclusion
Preparing a bank reconciliation statement ensures that businesses maintain accurate records, detect irregularities at the earliest stage, and uphold financial credibility. By integrating reconciliation into routine processes, organizations can safeguard cash flow, streamline audits, and build a foundation for sustainable financial growth.
Upgrade your accounting today with LOGIC ERP accounting software and see how automation makes BRS effortless. Call at +91-73411-41176 or send us an email at sales@logicerp.com to book a free demo today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is BRS in simple words?
BRS is a reconciliation of the Balance with the Bank and the Balance in books.
2. What is the full form of BRS in accounting?
BRS full form is Bank Reconciliation Statement.
3. Why is BRS important in business?
It detects errors, prevents fraud, and ensures accurate financial records.
4. What are the common causes of differences in BRS?
Outstanding cheques, bank charges, direct deposits, errors, etc.
5. Is BRS prepared monthly or annually?
BRS is generally prepared monthly, but businesses can prepare it anytime for reconciliation.