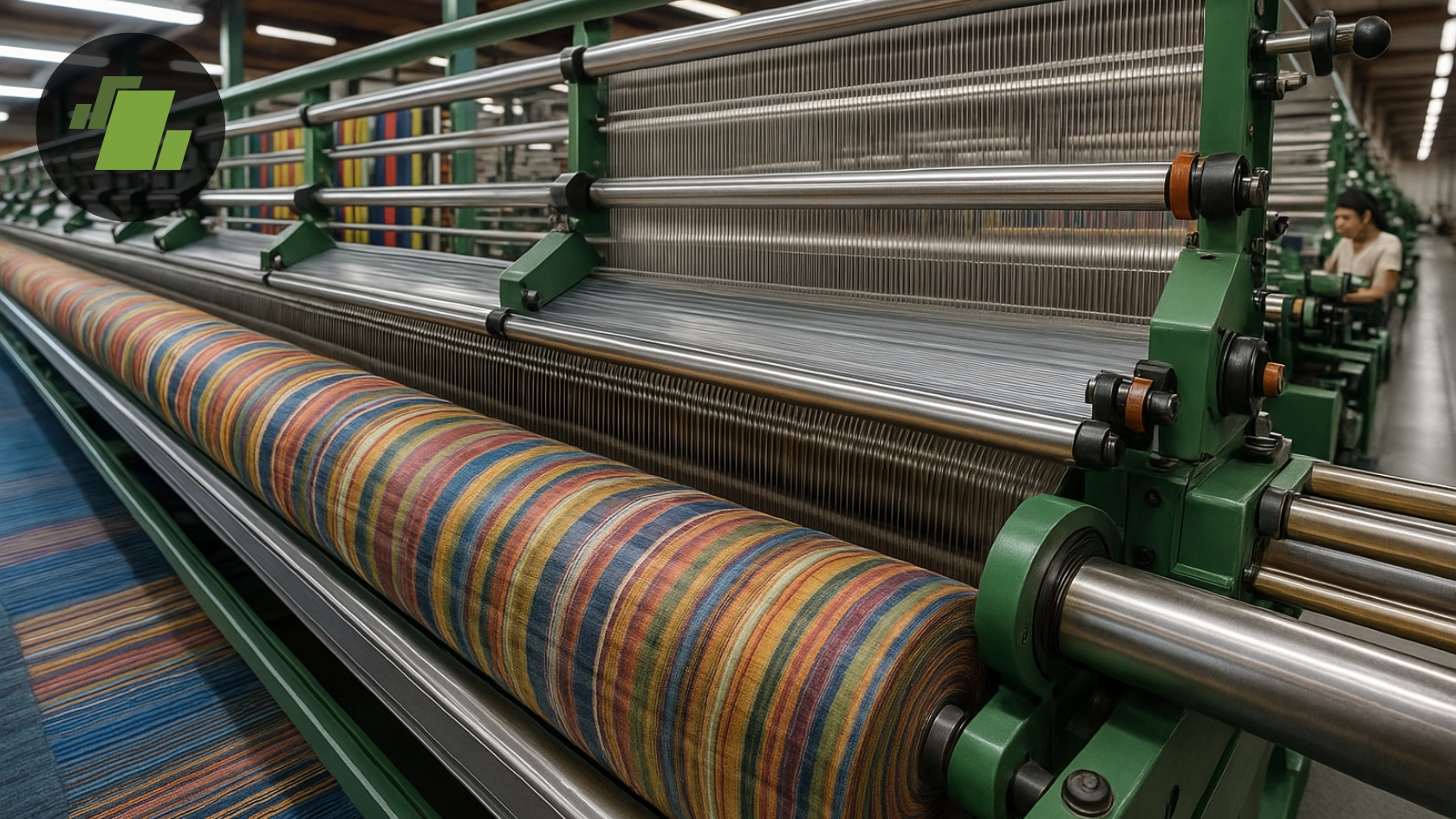

Streamline operations with textile and apparel manufacturing software—optimize production, inventory and costs. Get LOGIC ERP for smarter business control. Book Demo Today!
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is software that stores all of a company’s data and supports it in delivering information at the appropriate moment. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) dates back to the 1960s and has achieved widespread adoption in the industry during the last two decades. Enterprise Resource Planning software is a collection of converging and highly centralizing industry application software components that distribute a frequently updated database containing core manufacturing and administrative functions such as accounting, planning, finance, purchasing, supply chain, manufacturing, marketing, and sales.
Components of ERP:
To satisfy increasingly complicated business requirements, ERP offers a variety of unique capabilities and add-ons. There are six major components of ERP, including:
-
Financial Management
-
Inventory Management System
-
Supply Chain Management
-
Business Intelligence
-
Customer Relationship Management
-
Human Resources
Working in Industries Using Enterprise Resource Planning Systems (ERP)
The deployment of enterprise resource systems is not a simple or straightforward process that yields immediate results. In reality, firms confront a slew of issues when attempting to implement enterprise resource systems, which can quickly devolve into nightmares. The enterprise resource planning system is built around a single comprehensive database. The database collects information and feeds it into modular systems that support practically all of the company’s business operations spanning divisions, functions, and locations across the world. When new data is entered in one spot, the linked data is updated automatically. The enterprise resource planning system is not adaptable, despite its ability to integrate. It’s a generic technique that doesn’t always take into account the unique peculiarities of each company.
Need of ERP:
Below mentioned are few reasons why your company needs ERP.
-
To meet delivery deadlines.
-
To optimize production schedules.
-
To forecast demand proactively.
-
To reduce labor work.
-
To get reduced lead times.
-
To get detailed analysis reports.
-
To maintain accurate records.
-
To manage and control costs.
Enterprise Resource Planning in Textiles: Key Features
-
Smooth flow of information within and outside the company.
-
Inherent functions for a need-based application.
-
A consistent technology framework enabling a high volume of transactions.
-
Easy access to visual dashboards.
-
Real-time monitoring of production orders.
-
Availability of raw materials is tracked automatically.
-
Automatically plan and control for production/sourcing.
-
Spinning, knitting, weaving, and dyeing processes are managed automatically as a single system.
Read More: Key Features of LOGIC ERP for Textile Industries in India
ERP Life Cycle in Apparel and Textile Industries
Any ERP software life cycle is similar to the typical software development life cycle. Designing, development, full growth, and decline are some of the stages. The adoption of ERP in the textile and garment industries will take place in four stages: evaluation, assortment, execution, and post-implementation. The following are the several processes involved in the ERP life cycle in the textile and apparel industry.
-
Investment decision in ERP system
-
Assessment of available ERP systems
-
Assortment of ERP systems
-
Prerequisite analysis of the vendor
-
Expanding and modifying the ERP system
-
Execution
-
End-user Training
-
An equivalent run of ERP software and accessible practices
-
Exist run by the ERP system
-
Periodic system updates and error fixing
-
Constant usage
-
Substitute for the available ERP system
Read More: Key Features of LOGIC ERP Solution | Best Apparel Cloud Software 2025
Functions of ERP Software in the Textile and Apparel Industry
-
Dye house management
The dyeing process produce a lot of waste, which is likely to raise the price of the fabric. The dye house management can utilize ERP software to keep track of how much dye is being used. In their basic ERP system, they supply chemical inventory, daily waste generation reports, recipe creation, dyeing lab management, batch management system, real cost calculation of reprocessed dyeing, and so on.
-
Cost
Merchandisers’ pre-costing of goods and real-time costing of raw materials on the production floor.
-
Production
Phases of production include a breakdown of utilization, beginning and ending dares, waste computation, and production progress monitoring.
-
Procurement
Requests, permissions, the format of purchase orders, and product delivery via document delivery.
-
Inventory
Availability of raw materials, final products by lot, package, batch-by-batch, work-in-progress, and order-by-order.
-
Access to sales order
Color, size variations, premade invoices, shipping papers, sales invoice, finished product selection, package list generation, and letter handling of credit facilities are all factors to consider.
Barriers in Implementing an ERP System
Below mentioned are the most significant roadblocks in implementing an ERP system.
-
Lack of a right project team, and apparent view of the ERP function.
-
Implementation at a higher cost
-
Consumer training and education
-
Top management support is limited
-
Change of resistance
Conclusion:
In the current industry, both basic software and textile-specific software packages are used. The challenges facing the textile and clothing sectors in implementing an ERP software appear to be similar to those faced by other manufacturing industries. Although e-commerce exists in the form of classic electronic data interchange with many improvements, the textile sector does not employ electronic market places. Textile industries appear to integrate business intelligence, finance, production, and supply chain management systems into their ERP systems. A new ERP system analyzes a financial statement and forecasts stock needs to keep inventory at a healthy level automatically.
Recent ERP systems have resulted in improved prompt delivery, lower purchasing costs, lower inventory costs, lower wastages, improved client relationships, and shorter lead times. For a healthy corporate environment, such essential benefits have aided in expanding the scope of Enterprise Resource Planning in large, small, and medium businesses.
Get started now! Call +91-734 114 1176 or email us at sales@logicerp.com to schedule your demo and take the first step towards operational excellence with LOGIC ERP.